Position is always crucial, whether at work or on the football field, and poker is no exception. In the most popular variants of the game, like Omaha and Texas Hold’em, a solid understanding of position is so vital to success that it can often be the difference between winning and losing.
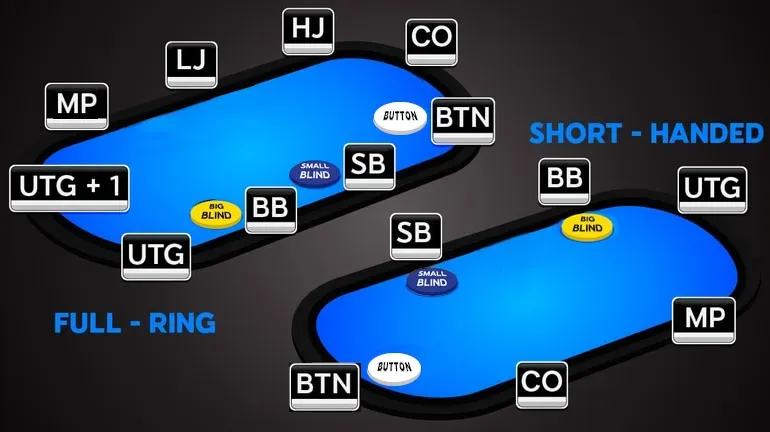
Poker table positions dictate the order of play.
They force people to act before others, which allows others to see what their opponents do before committing a chip to the pot. The later you act, the more information you have to work with, and the easier your decisions become.
There is a direct correlation between how late someone acts and how much they win, which is no coincidence. But it’s not all about what your opponents do either.
Good positional awareness can help you abuse a strong position, avoid putting yourself in bad situations, and know when it’s best to play dead. Before we get into any strategic nitty-gritty though, here’s a breakdown of all of the poker position names.
Poker Table Positions - The Blinds
Before any cards are dealt in a game of poker, there are two mandatory blind bets called the Big Blind and the Small Blind. The two players to the left of the ‘Dealer Button’ must pay them before each hand. The Dealer Button is a small disk that moves clockwise around the table to keep things fair.
These blind bets get the game going and are one of the game's most crucial yet underrated elements. Without them, players could see hand after hand for free and would only play if they had pocket aces. This action would lead to everyone breaking even and ruining the game..
Before we learn more about the blinds, let’s examine one of the most essential positions in poker: the ‘Button’.
Poker Table Positions - The Button (BTN)

The Button is the seat from which the cards are dealt. Traditionally, the person in this seat would deal, starting with the player to their left. But casinos usually have professional dealers who move the button at the start of the hand and deal as if they were the player in the button seat.
The Button is vital because all post-flop action starts with the player to their left. This fact makes the button one of the latest to act before the flop and last after that.
So, the Button gets more information - such as poker combos - than every other player does before risking chips, making it the most powerful of all poker table positions.
Poker Table Positions - Big-Blind (BB)
The Big Blind position is two to the left of the button and has the irritating task of stumping
up the biggest blind bet. Although the Big Blind is last to act in the first betting round, it is second to act after the Small-Blind on all subsequent betting rounds, which makes it challenging to play.
So much so, that most players lose more money in the Big Blind than in any other seat at the table.
Poker Table Positions - Small-Blind (SB)

The small blind position is to the direct left of the button. Like the Big Blind to their left, the
Small Blind (SB) has to post a mandatory preflop bet, typically half the size of the Big Blind (BB). Life sucks in general for the small blind.
As well as having to toss blind money into the pot, the SB is second to last to act before the flop. This fact makes it weaker than the BB since it never gets to close the action. It’s always first to go after the flop, too, so it has no idea what other players might do before acting.
Playing in the Small Blind is like being a guest at a family dinner after a sibling dispute. It’s awkward and uncomfortable, which is why it’s one of the most unprofitable positions in poker.
Poker Table Positions - The Cutoff (CO)
The cutoff position is to the direct right of the Button. It gets to act pretty late, both pre and post-flop, so it’s not the worst seat at the table. But an aggressive button player can make life pretty tricky for the Cutoff.
In hands where the Button folds before the flop, the Cutoff becomes the strongest seat at the table and is the last person to act post-flop.
Poker Table Positions - Hijack (HJ)
The Hijack is the position to the direct right of the Cutoff. This position is commonly called middle position (MP) when playing nine or ten-handed. Using the poker term ‘hijack’ is a good way to trick your friends into thinking you know what you’re talking about!
The Hijack follows the trend we’ve seen (and will see) with the other positions. It is weaker than the Cutoff and Button, who both act after it but stronger than any other position.
Poker Table Positions - Lojack (LJ)
The Lojack is the position to the direct right of the Hijack and is, therefore, slightly weakest. In a full-ring, 9-handed game, the Lojack is in a middle position. Despite the fancy name, it's not that strong preflop since it has to act after just a few other players.

If you’re playing 6-handed, you might hear people refer to this seat as ‘under-the-gun (UTG)’, which is just the cool kids’ poker lingo for ‘first to act. The Lojack would go first at a 6-handed table.
The phrase ‘under the gun’ (or UTG) describes the first player to act in any spot, meaning UTG’s exact position relative to the button will depend on the number of players at the table.
Though it's not that strong preflop, it's not too uncommon for the Lojack to have the luxury of acting last post-flop, especially if they raised first before the flop.
When the players in the Hijack, Cutoff, or Button get involved, the Lojack can find itself sandwiched between them, which is like sitting between bodybuilders on a cramped economy flight… Good luck getting an armrest there.
Middle Position (MP) and Early Position (EP)
Middle position doesn’t exist in shorthanded games, but in a full-ring context, it refers to any seats between the Lojack and the two players directly to the left of the blinds.
As we've seen so far, positions get weaker as they get earlier, which makes playing in middle position a bit like stepping in dog poo with your favourite shoes on. It could be better, but at least you weren't barefoot.
Early Position
Early position refers to the two seats immediately after the blinds. These are usually EP, EP+1, EP+2 or UTG, UTG+1, and UTG+2.
As already mentioned, there is no early position in a 6-handed game, with the Lojack acting first, but it’s still commonly referred to as “under-the-gun”.

In or Out of Position
Now that we've explained the different poker positions, it's time to learn a few essential phrases and how to put your knowledge into practice.
In poker, you will always be either in position or out of position against other players:
- If they act before you, you are in position.
- But they would have position on you if you were to act first.
Since poker is all about using information, it’s better to be in position.
How to Use Position as Part of Your Poker Strategy
The importance of position in poker can be shown by a training activity WSOPE Main Event champion Annette Obrestad did in 2007. Looking to improve her positional play, she decided to cover her cards and play a small-stakes tournament blind.
Though she did need to peek at her cards when faced with some all-in decisions, her positional understanding was so great that she won the event playing (mostly) blind. So, how did she do it?
Although you need to run well to win any tournament, Annette didn’t focus on poker hand rankings. Instead, she won because she used her positional advantage to pressure other players and outplay them when she was in position post-flop.
How Can Position Help

There are a couple of reasons why it’s better to be “in position” post-flop. Being in position allows us to see what our opponent does before us we have to make a decision.
We can make logical deductions based on whether he chooses to check or bet.
- If the board produces a scary turn or river card, we see how our opponent responds to it before acting.
- If they check, we might use this information to start bluffing, for example, or fold without losing any extra money if they keep betting.
Since they have to act first, our opponent must do so without any additional information about the strength of our hand.
Being in position allows you to control the size of the pot more easily, too. You get to make the final decision of the street.
- You can keep the pot small and see another card by checking back in position or just calling against a bet.
- You can also bet or raise if you want to build the pot.
Things are much trickier when you’re out of position. You can always check to try to see a free card, but there are never any guarantees because your opponent might bet.

It’s much tougher to control the action, too. While you can still bet when you want to build the pot, you cannot raise unless your opponent bets first. Likewise, if you want to pretend to be weak to check-raise the turn, the players in position can check back.
This scenario isn’t ideal as it gives them a chance to river the best hand or results in you scooping a much smaller pot.
Relative and Absolute Position
These two phrases might sound complicated, but they’re pretty straightforward:
Absolute Position
Absolute position means that a player is last to act in general on each postflop street. For example, in a heads-up pot between the BTN and CO, the BTN always has absolute position because they act after the CO on each street.
Relative Position
Relative position is a little different. Relative position means that a player is last to act on a particular street as a result of the flow of action. For example, if CO checks and BTN bets, CO now has relative position because they will act last after the BTN (unless there is a raise from another player).

The CO can end the action by calling or folding. They can even open things up again by tossing in a raise, which probably won’t make him too many friends!
One of the most common examples of relative position involves the blinds preflop. The SB and BB always act after the BTN in the first betting round, meaning they have relative position preflop.
They do not have absolute position because as soon as we reach the postflop betting rounds, the BTN will act after the blinds on each street.
Though there are many poker position names, try not to get too bogged down because position is a relatively simple concept. Understanding how to use position well is an ongoing challenge.
The game is constantly changing, and learning to manipulate position takes a lot of time and skill!